Forex Trading Secrets Revealed: How to Tap into the $6 Trillion Daily Market
The foreign exchange market, or Forex, is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world. With a daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion, it dwarfs other financial markets, such as stocks and bonds. Forex trading offers numerous opportunities for individuals and institutions alike to profit from fluctuations in currency values. However, to navigate this vast market effectively, traders must understand its mechanics, employ sound strategies, and manage risks wisely. This article will delve into the intricacies of Forex trading and reveal essential tips for tapping into this lucrative market.
Understanding the Basics of Forex Trading
What is Forex?
Forex trading involves the buying and selling of currencies to profit from changes in their exchange rates. Unlike other financial markets, Forex operates without a centralized exchange, relying instead on a global network of banks, brokers, and traders. This decentralized structure allows for 24-hour trading, spanning major financial centers such as London, New York, Tokyo, and Sydney.
Currency Pairs
Forex transactions involve trading currency pairs. Each pair consists of a base currency (the first currency) and a quote currency (the second currency). For example:
- EUR/USD: Euro (base) and US Dollar (quote)
- GBP/JPY: British Pound and Japanese Yen
The value of a currency pair represents how much of the quote currency is needed to purchase one unit of the base currency. If EUR/USD is trading at 1.10, it means 1 Euro equals 1.10 US Dollars.
Bid, Ask, and Spread
- Bid Price: The price at which you can sell the base currency.
- Ask Price: The price at which you can buy the base currency.
- Spread: The difference between the bid and ask prices, representing the broker’s profit margin.
The Mechanics of Forex Trading

Leverage and Margin
One of Forex trading’s most appealing aspects is the use of leverage. Leverage allows traders to control larger positions with a relatively small amount of capital. For instance, with a leverage ratio of 100:1, a trader can control a $100,000 position with just $1,000.
However, leverage is a double-edged sword. While it amplifies potential gains, it also increases the risk of significant losses. Margin refers to the funds required to open and maintain a leveraged position. If a trade moves against the trader, the broker may issue a margin call, requiring additional funds to cover potential losses.
Market Participants
The Forex market is driven by various participants, each with unique goals:
- Central Banks: Influence currency values through monetary policy and interventions.
- Commercial Banks and Financial Institutions: Facilitate large-scale Forex transactions.
- Hedge Funds: Engage in speculative trading to profit from currency fluctuations.
- Retail Traders: Individual traders seeking to capitalize on market movements.
Types of Forex Trading Strategies
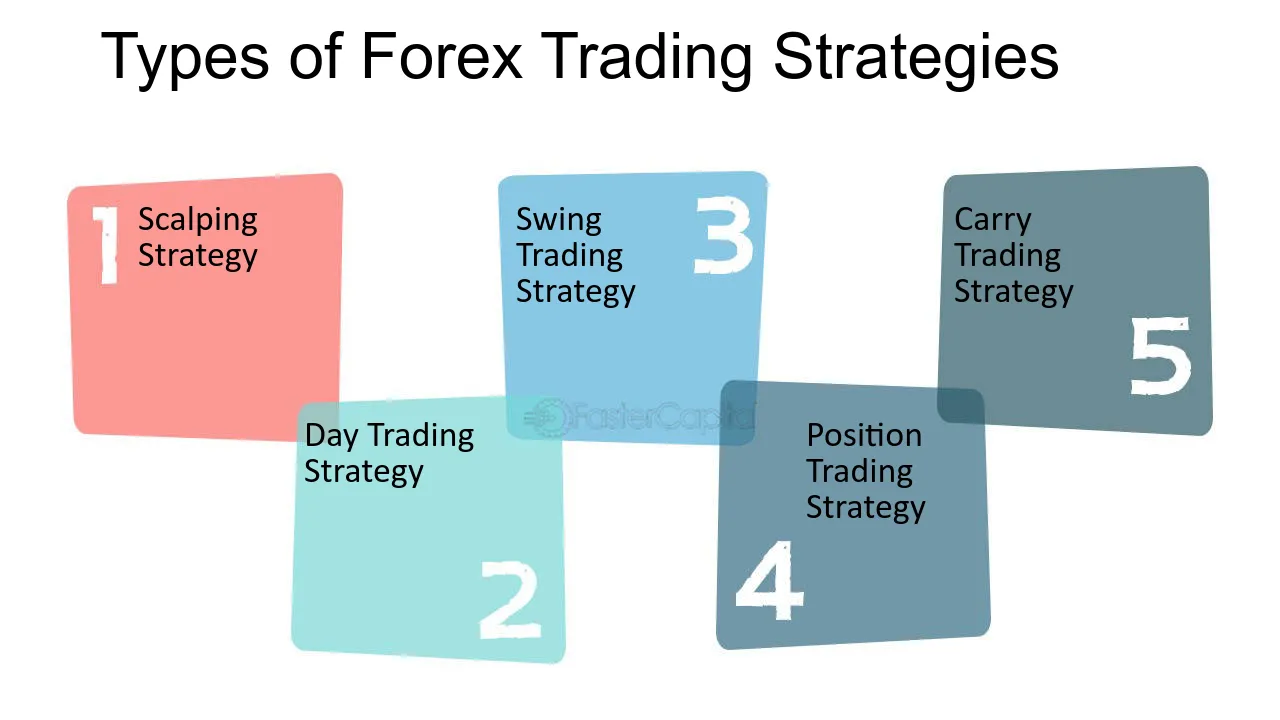
Successful Forex trading requires a well-defined strategy. Here are some popular approaches:
1. Day Trading
Day traders seek to capitalize on short-term price movements, often holding positions for hours or minutes. This strategy requires:
- Constant market monitoring.
- Quick decision-making.
- Strict risk management.
2. Swing Trading
Swing traders aim to profit from medium-term trends, holding positions for several days or weeks. They rely heavily on technical analysis to identify entry and exit points.
3. Scalping
Scalping involves making numerous small trades throughout the day to profit from minor price changes. It’s a high-frequency strategy that demands precision and focus.
4. Position Trading
Position traders adopt a long-term approach, holding positions for months or even years. They base their decisions on fundamental analysis, considering factors such as interest rates, economic data, and geopolitical events.
Analyzing the Forex Market
To succeed in Forex trading, traders must analyze the market using two primary methods:
1. Technical Analysis
Technical analysis involves studying historical price charts and using indicators to predict future price movements. Popular tools include:
- Moving Averages: Help identify trends.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Indicates overbought or oversold conditions.
- Fibonacci Retracements: Identify potential support and resistance levels.
2. Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis focuses on macroeconomic factors that influence currency values, such as:
- Interest Rates: Higher rates typically attract foreign investment, boosting the currency.
- Economic Data: GDP growth, employment figures, and inflation rates provide insights into a country’s economic health.
- Geopolitical Events: Political stability and international relations can significantly impact currency markets.
Risk Management in Forex Trading
The Forex market’s high volatility presents both opportunities and risks. Effective risk management is crucial to long-term success. Here are some key principles:
1. Use Stop-Loss Orders
A stop-loss order automatically closes a trade when the price reaches a predetermined level, limiting potential losses.
2. Diversify Trades
Avoid putting all your capital into a single trade or currency pair. Diversifying reduces the impact of adverse market movements.
3. Manage Leverage
While leverage can enhance profits, excessive use can lead to substantial losses. Use leverage cautiously and ensure you understand its risks.
4. Risk-Reward Ratio
Maintain a favorable risk-reward ratio—the potential profit should outweigh the potential loss. A common practice is a 1:3 ratio, where the potential gain is three times the risk.
Tools and Platforms for Forex Trading

To access the Forex market, traders use online trading platforms provided by brokers. These platforms offer various tools to enhance the trading experience, including:
- Real-time Price Charts: Visual representation of market movements.
- Economic Calendars: Track important events and data releases.
- Automated Trading Systems: Execute trades based on pre-set criteria.
Popular trading platforms include MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), and cTrader.
Forex Trading Psychology

Successful trading requires more than technical knowledge—it demands emotional discipline. Here’s how traders can manage their mindset:
1. Avoid Emotional Trading
Emotions like fear and greed can lead to impulsive decisions. Stick to your trading plan and avoid chasing losses.
2. Stay Patient
Forex trading involves periods of uncertainty and market fluctuations. Patience is key to identifying the right opportunities.
3. Learn from Mistakes
Every trader experiences losses. Analyze your trades, identify mistakes, and use them as learning opportunities to refine your strategy.
Forex Trading Regulations
Forex trading is subject to regulation to protect traders and ensure market integrity. Regulations vary by country, but reputable brokers are typically licensed by regulatory authorities such as:
- Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) in the US.
- Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK.
- Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC).
Traders should choose brokers that comply with these regulations to ensure a safe trading environment.
Conclusion
Forex trading offers vast opportunities for profit, but it requires knowledge, strategy, and discipline. By understanding the market’s mechanics, employing effective trading strategies, and managing risks, traders can tap into the $6 trillion daily market and achieve financial success.
Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced trader, staying informed and continuously improving your skills is essential. For more insights and tips, explore advanced trading resources or try innovative tools like Hix AI, a powerful alternative to traditional trading assistants.